- Web hosting
- Services
- Help
Knowledge base
Configuring a Mail Client to work with a mail server
If your hosting service has a mail server running on it, you can send and receive email using a mail client on your local computer (Outlook, Mozilla, Thunderbird, etc.).
Client can be configured manually or automatically.
To configure manually, open the mail client on your local computer and add a new account. For Outlook, go to the "File" menu and select "Add Account":
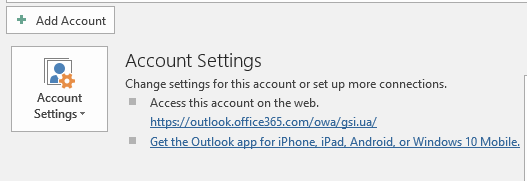
Select the manual mode.
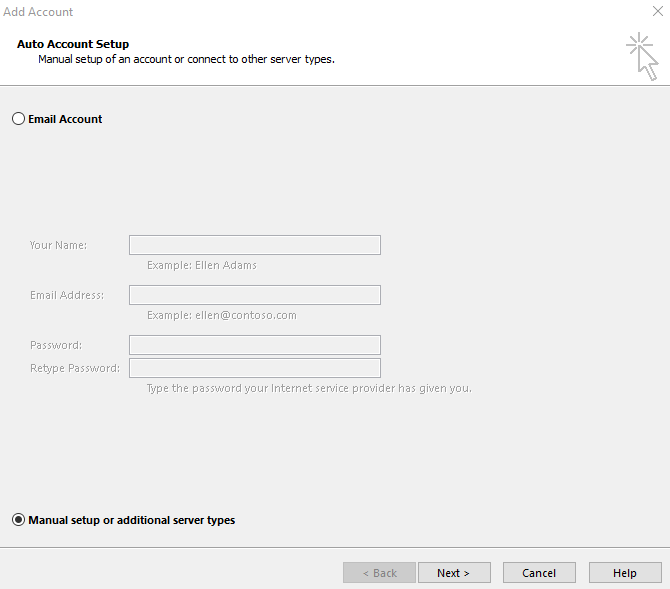
Specify the "POP or IMAP" protocol.
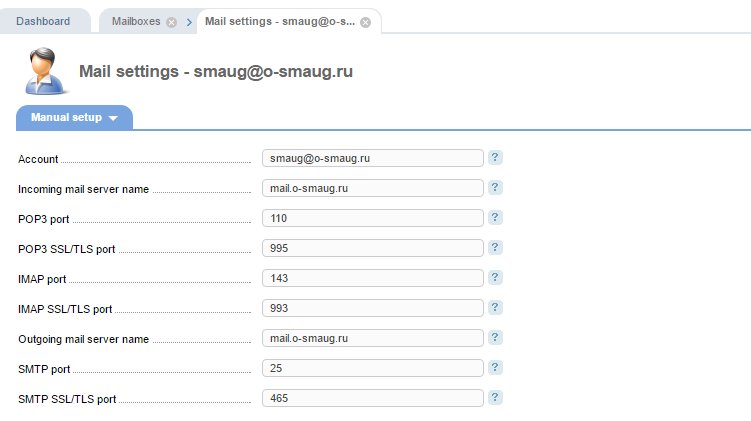
In the pop-up window, fill out the fields with the applicable account information. To obtain this information, open the ISPmanager control panel and go to "Accounts" -> "Mailboxes" (for ISPmanager 5 version).
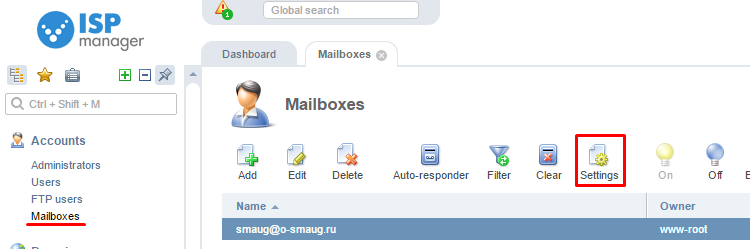
Click on the name of the mailbox, then click the "Settings" button.
The pop-up window contains to the data needed to manually configure the mailbox. Copy and paste the server names for both the incoming and outgoing mail into the customizable mail client (your client may not be identical to the provided example).
For Outlook, the account settings are as follows:
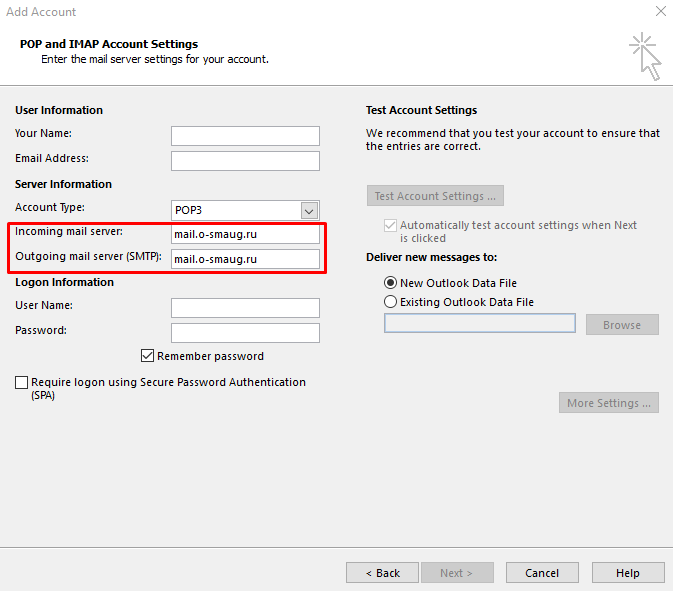
The account type can be both POP and IMAP (the example demonstrates IMAP).
The log in user name is the part of your email address before the “@” sign. For example, if your email address is smaug@smaug.smaug.com, then the username to log in is smaug.
To automatically configure an account, download the configuration file from ISPmanager under "Auto setup" ("Accounts" -> "Mailboxes" -> "Settings").
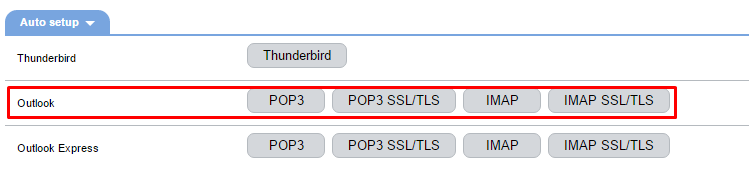
Run the configuration file and reboot the computer.
Run the email client, add a new account and fill out the form. For Outlook, these fields are as follows:
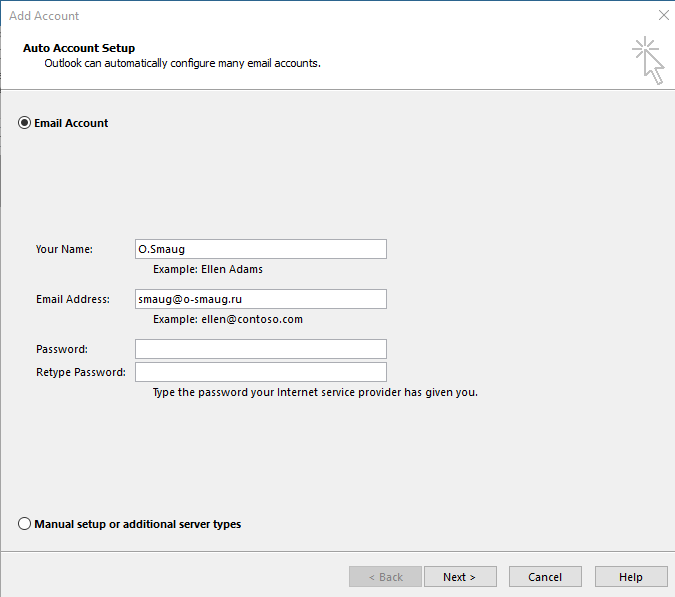
If you are using a different mail client, the configuration is the same, given that:
- the server name is generally a mail.your_domain name (for example, if your email is smaug@mydomain.com, then the server name is mail.mydomain.com) or IP address;
- the log in username for the mail server is is the part of your email address before the “@” sign (for example, if your email address is smaug@mydomain.com, then the log in for the mail server is smaug);
- enable authorization to send mail (user authentication) using the same credentials utilized for receiving mail;
- lastly, to receive mail, you can use both POP and IMAP protocols, and sending always requires the SMTP protocol using port 25 with port 587 as an alternative.
